Food Nutrients
CARBOHYDRATES
- Examples are sugars, starches (pasta, potatoes, flour) and cellulose (fibre)
- Contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms as 2H : 1O
- An immediate source of energy for the body
- In the process of respiration, glucose sugar and oxygen give energy and wastes of carbon dioxide and water.
- 3 forms of carbohydrates are:
- Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars e.g. glucose in honey, and fructose in fruit)
- Disaccharides (Double Sugars e.g. sucrose, lactose, maltose)
- Polysaccharides (e.g. starch, cellulose)
- All carbohydrates are broken down to simple sugars (monosaccharides) by enzymes in the digestive tract
PROTEINS
- Examples are meat, eggs, beans
- Some body proteins are muscle, haemoglobin, hormones and enzymes
- Long-chain molecules made of amino acids
- Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and usually sulphur and phosphorus
- Used to repair and build body tissues, but can be used as a last source of energy
- Digestive enzymes break down proteins into amino acids
- There are over 30 amino acids. Plants can make their own amino acids from simpler substances. However, cannot synthesise about 20 amino acids, so must eat them in the diet. These 20 are called essential amino acids.
LIPIDS (FATS AND OILS)
- Examples are butter and oils
- Contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
- Each molecule is composed of 1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid molecules
- Bile and digestive enzymes break down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
- Used as a source of energy, as a structural and an insulating material
VITAMINS
- Help to control chemical reactions in the body
- Are only required in small amounts
- Deficiencies and excesses of vitamins may cause disease
| VITAMIN | SOURCE | EFFECTS OF DEFICIENCY |
| A (retinol) | Carrots, tomatoes, leafy vegetables, egg yolk, milk, cheese | Poor night vision, skin infections |
| B1 (thiamine) | Wholemeal bread, eggs, milk, cheese | Beriberi (loss of appetite, weakness) |
| B2 (riboflavin) | Eggs, milk, cheese, yeast | Pellagra (skin infections, mental illness) |
| C (ascorbic acid) | Citrus fruit, green vegetables | Scurvy (bleeding gums, loss of teeth) |
| D (calciferol) | Eggs, cod liver oil, butter, milk | Rickets (deformed bones) |
| E (tocoperol) | Green vegetables, wheatgerm, milk | Anaemia |
| K (phylloquinone) | Green vegetables | Impairs blood clotting |
MINERAL IONS
- e.g. salts containing sodium, calcium etc.
- Help build strong bones and teeth, needed for healthy nervous function, and used in the clotting of blood
- Lack can cause disease
| MINERAL | SOURCE | EFFECTS OF DEFICIENCY |
| Calcium | Milk, cheese, green vegetables | Rickets (poor bones and teeth) |
| Iron | Meat, eggs liver, vegetables | Anaemia |
| Iodine | Fish, water | Goitre (poor growth and development) |
| Fluorine | Drinking water | Poor teeth |
| Phosphorus | Dairy foods, eggs, meat, vegetables | Poor bones, teeth and muscles |
| Potassium | Meat, fruit, vegetables | Affects nerves, muscles and blood |
| Zinc | Green vegetables, onions, liver | Part of the hormone called insulin |
Tests for Chemical Components of Food
| CHEMICAL | TEST | POSITIVE RESULT |
| Protein | Add a few drops of copper sulphate solution to the food sample, then a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution and mix well. | Blue-purple |
| Starch | Add a few drops of iodine solution to the food sample. | Blue-black |
| Glucose | Add an equal volume of Benedict's solution to the food sample and warm in a very hot water bath for a few minutes. | Orange-red |
| Lipid (Fats and Oils) | Rub a food sample onto brown paper and allow to dry. | Translucent spot |
Rub a food sample onto brown paper......
The Human Digestive System
Processes in Digestion
- Ingestion - the mechanical taking in of food, chewing and swallowing
- Digestion - The breakdown of food into smaller particles by physical or chemical means
- Absorption - the absorption of these smaller food particles from the digestive tract into the blood
Types of Food Breakdown
- Physical or Mechanical Breakdown - e.g. chewing, mixing with bile
- Chemical Breakdown - e.g. enzymes, hydrochloric acid
Parts and Functions of the Human Digestive System
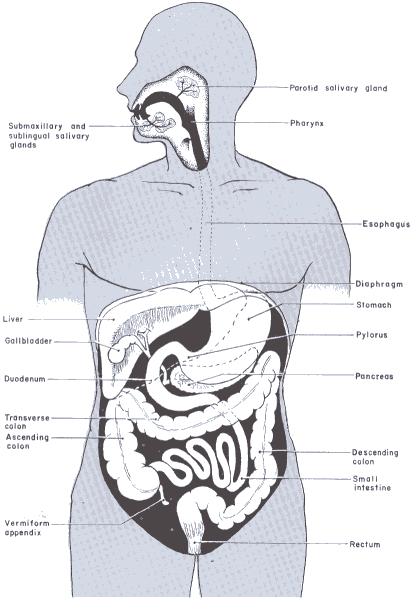
Mouth
- Ingests food
- Teeth physically break down food by chewing
- Saliva lubricates food
- The enzyme, salivary amylase also called ptyalin, breaks down starch into simple sugar, glucose
Pharynx
- At the back of the mouth cavity
- Both food and air pass through here
Oesophagus
- Tube between mouth and stomach
- A flap called the epiglottis closes over the top of the windpipe or trachea when swallowing, so that food does not enter the respiratory tract
- The walls of the digestive tract from the oesophagus to the anus are muscular, and contract rhythmically to move food. The muscular contractions are called peristalsis.
Stomach
- 2 circular muscles called sphincters surround the entry and exit of the stomach to control the flow of food
- Food remains in the stomach for about 3 hours where it physically broken down by the churning muscular contractions of the stomach wall muscles
- Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid and has a pH of 1 without food, and 3 with food.
- HCl helps to kill bacteria, and works in association with the enzyme, pepsin, to partially break down proteins.
- The stomach lining contains mucus to prevent damage from the acid
- Only alcohol and a few drugs can be absorbed through the stomach wall into the blood
Small Intestine
- Long tube that is about 7 metres long and 2.5 centimetres in diameter
- 3 parts of the small intestine are duodenum, jejunum and ileum
- Most of digestion occurs in the small intestine
- The enzymes of the small intestine do not function on the acidic stomach contents. First, an alkaline substance from the pancreas is secreted into the duodenum to neutralise the stomach acid.
- A green substance called bile that is made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder is released into the duodenum to break the large fat particles into smaller fat particles
- Enzymes from the pancreas also break down food chemically. Amylase breaks starch into simple sugars. Lipase breaks lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. Peptidases and Trypsin break down proteins into amino acids.
- After the food into broken into smaller particles, it is absorbed through finger-like projections called villi on the walls of the small intestine into blood capillaries.
Large Intestine
- Thicker in diameter than the small intestine
- Water is absorbed from the remains of undigested food to make faeces
- Bacteria produce Vitamin B in the large intestine
- Mucus lubricates the faeces
- The appendix is attached to part of the large intestine. It may be part of the body's immune system.
- Diarrhoea is the condition of more liquid faeces when the large intestine is infected.
Rectum
- Storage area for faeces at the end of the large intestine
- There is a sphincter surrounding the anus, the hole through which faeces passes on defaecation.
- Constipation is the condition of dry hard faeces as a result of low fibre in the diet.
The Role of the Liver in Digestion
- Bile - The liver produces bile which is stored temporarily in the gall bladder, and then is secreted into the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) for the emulsification of lipids. Bile is also alkaline and aids in the neutralisation of stomach acid in the small intestine.
- Sugar Conversion - After a meal, excess simple sugars in the bloodstream pass to the liver and are converted and stored as glycogen. However, between meals, the glycogen is converted back to simple sugars and released into the bloodstream. In this way, the blood sugar remains constant.