Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction is the formation of a new organism where there is the presence of a single parent, and no joining of gametes (e.g. sperm, pollen, egg). The offspring has identical genes and chromosomes to the parent.
- Advantages of Asexual Reproduction - No energy is expended to find a mate. There is a high chance of survival of the offspring, if the offspring remains near the parent in a stable environment.
- Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction - Less genetic diversity gives the offspring a lesser chance of survival if the environment changes.
- Examples of Asexual Reproduction:
- Binary Fission (e.g. of bacteria and Amoeba) occurs when a cell simply grows larger, replicates its DNA in genes and chromosomes, and then forms a cell membrane down the mid-section of the cell to form 2 new 'daughter' cells.
- Budding (e.g. of yeast and hydras) occurs when a small part of the parent's body separates from the rest and develops into a new individual, eventually either becoming an independent organism or part of an attached colony.
- Spore Formation (e.g. of ferns, malaria-causing protozoan called Plasmodium) occurs where special cells with resistant coverings form. These coverings are resistant to unfavourable environmental conditions such as heat, cold or dryness.
- Fragmentation (e.g. of flatworms and starfish) occurs when a parent body is broken into pieces, and each piece may form a new individual.
- Regeneration (e.g. of many plants) occurs when part of an organism grows to form other organisms that are often still connected to the original organism. Examples of regeneration in plants are the vegetative propagation of runners of grasses and strawberries, rhizomes in ferns, tubers in potatoes, and growing plants from cuttings.
- Parthenogenesis (e.g. of bees, wasps, some cockroaches, and liver flukes inside a host) occurs when a new organism develops from an unfertilised egg. For example, in honeybees, the female or queen honeybee is inseminated just once in her lifetime. The sperm she receives are stored in a little pouch connected to the genital tract, and closed off by a muscular valve. As the queen lays eggs, she can either open this valve permitting sperm to fertilise them (to become female queens or female workers), or she can keep the valve closed so that unfertilised develop into male drones.
Sexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction is the formation of a new organism from 2 parents usually, and involves the joining of gametes (e.g. sperm, pollen, egg) to form a single cell called a zygote (or fertilised egg). The offspring are similar, but not identical to the parents.
- Advantages of Sexual Reproduction - There is greater genetic variation of the offspring and therefore, greater chance of survival in changing environments.
- Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction - Energy is expended in finding a mate in many organisms. However some organisms have both male and female reproductive organs that are able to produce gametes simultaneously.
Introduction to Human Reproduction
- Gametes are the reproductive cells. The male gamete is called the sperm in many animals, and pollen in many complex plants. The female gamete is called the egg or ovum (Plural: ova).
- Gonads are the reproductive organs that produce gametes and sex hormones. The human male gonad is called the testis (Plural: testes), and the female gonad is the ovary.
- Puberty is the time during teenage years when males start to produce sperm, and females start to release eggs. Puberty occurs a couple of years earlier for females than males usually.
- Menopause is the time when females stop releasing eggs. This usually occurs between 45 to 55 years of age. However, males do not undergo menopause and produce sperm all their lives following puberty.
The Human Male Reproductive System
THE PATH THAT SPERM TRAVEL
Testes
![]()
Epididymis
![]()
Vas Deferens (or Sperm Duct)
![]()
Urethra
PARTS OF THE HUMAN MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
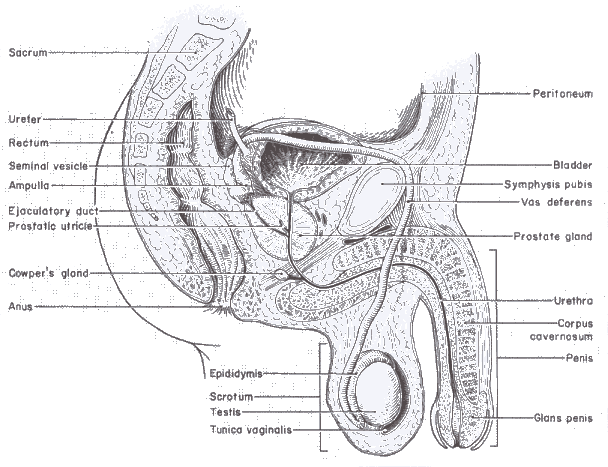
Testis
- There are 2 testes situated in a sac called the scrotum
- Produces sperm in large numbers in seminiferous tubules
- Produce male sex hormone called testosterone which regulates sperm production and secondary sexual characteristics (e.g. hair on face chest armpits and pubic area, deep voice, muscle bulk)
Epididymis
- Stores the large numbers of sperm until they are ejaculated out through the penis
Sperm Duct or Vas Deferens
- Transports sperm from the testis to urethra
Semen-Producing Glands
- Semen is the fluid produced to protect the sperm from dehydration and the acidic environment of the female vagina after sexual intercourse. Semen also allows the sperm to swim more easily.
- Semen - producing glands are Cowper's Gland, the Seminal Vesicles and the Prostate Gland.
Urethra
- This is the tube that normally carries urine from the urinary bladder.
- When semen containing sperm is ejaculated, it also travels out through the urethra, but the prostate gland enlarges to block off any urine from the bladder at that time.
Penis
- The urethra is the tube inside the penis.
- During sexual intercourse, the spongy cells that surround the urethra fill with blood, and the penis becomes firm and erect.
The Human Female Reproductive System
THE PATH THE EGG TRAVELS
Ovary
![]()
Oviduct or Fallopian Tube
![]()
Uterus or Womb
![]()
Cervix
![]()
Vagina
PARTS OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
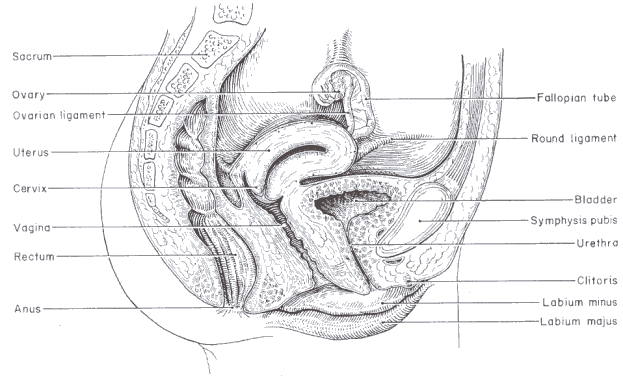
Ovary
- There are 2 ovaries
- Produces eggs or ova, female sex hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) that regulate the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and the secondary sexual characteristics (e.g. pubic and underarm hair, breasts, enlarged hips)
- At birth, females have all their eggs formed, but in an immature state
- After puberty and before menopause, one egg is released about every 28 days from each ovary
Oviduct or Fallopian Tube
- Connects between ovary and uterus
- Place where conception or fertilisation of an egg by a sperm occurs
Uterus or Womb
- Strong muscular and elastic organ where an unborn baby develops
- After an egg is released from the ovary, a blood-filled lining develops on the walls of the uterus in preparation for the nourishment of the unborn baby. If no fertilisation of the egg occurs, then this lining passes out through the vagina over several days as 'periods' or menstruation.
Cervix
- The opening between the uterus and the vagina
- During pregnancy, a mucous plug forms across the cervix separating the uterus from the outside to prevent infection of the unborn baby. This plug falls out, and the cervix dilates before the birth of a baby.
Vagina
- Place where the penis is inserted during sexual intercourse
- An elastic and muscular organ that expands during birth to allow for the passage of the baby
THE FEMALE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
- The menstrual cycle begins at puberty and ceases at menopause.
- It takes about 28 days.
- Menstruation is regulated by the female sex hormones, oestrogen and progesterone.
- Day 1 is the day when menstruation or 'periods' begin
- Menstruation - Menstruation or 'periods' is the release of the blood-filled lining of the uterus if a woman is not pregnant. It lasts about 5 days.
- Ovulation is the release of the egg from the ovary between about Days 12 to 16.
- A woman will become pregnant if fertilisation (the joining of the egg and the sperm) occurs several days after ovulation when the egg is in the fallopian tube. During pregnancy, menstruation ceases.
FERTILISATION OR CONCEPTION
- After sexual intercourse, the sperm travels up to join with the egg in the fallopian tube
- The single-celled fertilised egg is called a zygote
- 23 chromosomes of the sperm and 23 chromosomes of the egg combine in the zygote's nucleus, so that the developing baby has 46 chromosomes
GESTATION OR PREGNANCY
- Gestation in humans lasts about 40 weeks or 9 months
- The first sign that a woman is pregnant is usually absence of menstruation ('no periods')
- After fertilisation in the fallopian tube, the zygote multiplies to form a ball of cells which travels down to the uterus
- The ball of cells (embryo) implants into the wall of the uterus
- At the place where implantation occurs, an organ called the placenta develops
- The umbilical cord grows between the placenta and the unborn baby's navel
- Inside the umbilical cord are blood vessels which provide nutrients and oxygen to the baby, and return wastes such as carbon dioxide back to the mother's bloodstream
- As the baby grows, it is called a foetus
- The foetus is protected by amniotic fluid inside an amniotic sac
- In the ninth month of pregnancy, the foetus turns upside down, and the mother's breasts enlarge ready for milk production
BIRTH
- At about 9 months, the 'plug' at the cervix releases, the amniotic sac breaks and fluid comes out through the vagina ('breaking of the waters')
- Muscular contractions occur to both dilate the cervix, and 'push' out the baby head first from the uterus
- Further muscular contractions expel the placenta
- The umbilical cord is cut close to the baby's navel
- The mother begins breast milk production
- The mother begins the menstrual cycle again, after the lining of the uterus from the pregnancy has been expelled over several days
- Breech Birth occurs when the baby is born legs first
- Caesarean Birth is the surgical removal of the baby from the mother's uterus
- Twins - Identical Twins (i.e. 2 sisters or 2 brothers) form when one egg and one sperm join, but as the zygote multiplies to form a ball of cells, the ball splits and the 2 embryos implant separately into the wall of the uterus. Non-identical or Fraternal Twins are formed when 2 eggs are fertilised by 2 sperm.
Plant Reproduction

Parts of a Flower
- Flower - a modified stem with modified leaves (sepals and petals) and sexual organs (male stamen or female pistil)
- Flowers may contain only male reproductive organs (staminate flowers), or only female reproductive organs (pistillate flowers), or both.
- The development of flowers is often following periods of either long or short nights. However, some angiosperms flower at any time of the year.
Pollination & Fertilisation
- Pollination is the transfer of the male pollen grain from the anther to the stigma of the female pistil. Pollination may occur by means of the wind or by animals such as bees.
- Self-pollination - pollination within the same plant
- Cross-pollination - pollination with another plant
- Fertilisation - the process when a male pollen grain enzymatically 'drills' a pollen tube down the style to the ovary, and then fuses with or fertilises a female ovum to form a single-celled zygote
The Fruit
- Fruit - the enlarged fleshy ovule (part of the ovary) which contains the seed that developed from the zygote
Germination of the Seed
- Germination - the growth of the seed into a small plant called a seedling
- Water is essential for germination
- Some Australian native plants also require short periods of high temperatures resembling bushfires in order to germinate.
- Seeds may be dispersed or spread by wind (e.g. pine seed), by water (e.g. coconut) or by animals (e.g. bird).